Introduction to Entity Framework Core
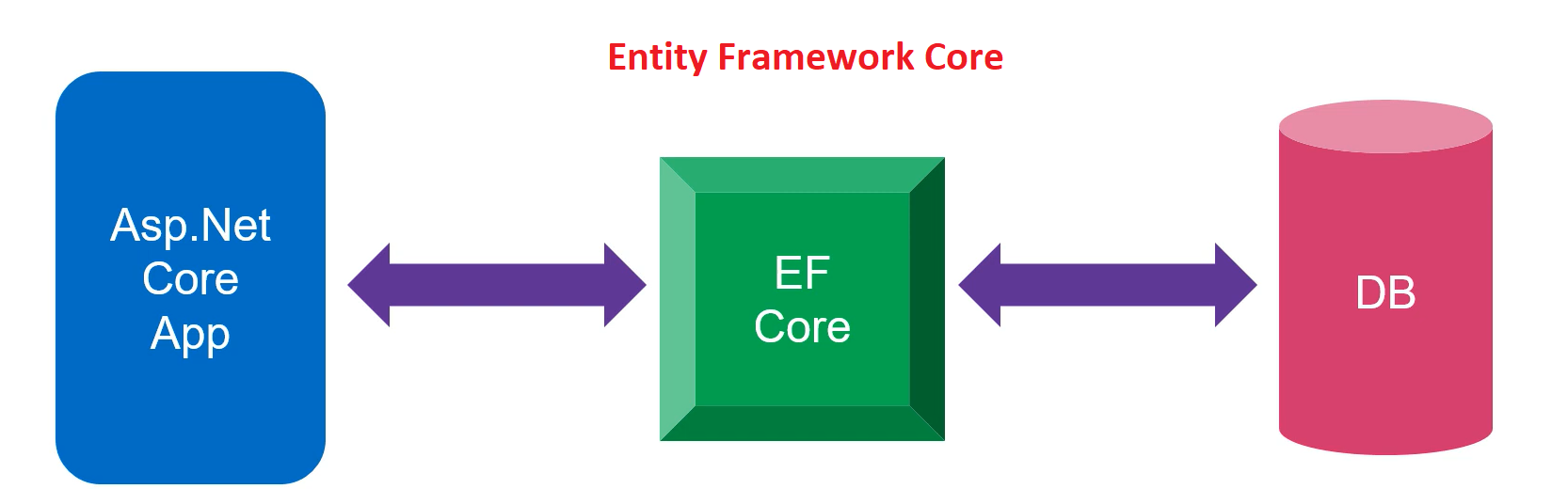
Entity Framework Core (EF Core) is a lightweight, extensible, open-source, and cross-platform version of the popular Entity Framework data access technology. It serves as an Object-Relational Mapper (ORM), enabling .NET developers to work with a database using .NET objects.
What is Entity Framework Core?
Entity Framework Core is an ORM that allows you to create a model by writing C# classes (POCOs), and that model will be used to interact with your database. This means you can create, read, update, and delete records in your database using these classes rather than writing SQL queries.
Key Features of EF Core include:
- Cross-Platform: EF Core works across different platforms like Windows, Linux, and Mac.
- Modeling: Using EF Core, you can map your domain classes with the database schema and optionally fine-tune the database schema using Data Annotations as well as Fluent API to fit your needs.
- Querying: EF Core allows you to use LINQ Queries against the database, which then get translated to SQL queries.
- Change Tracking: EF Core keeps track of changes that occurred to instances of your entities as you manipulate them.
- Saving Data: EF Core provides the mechanism to save changes in the database that were made in the application's domain objects.
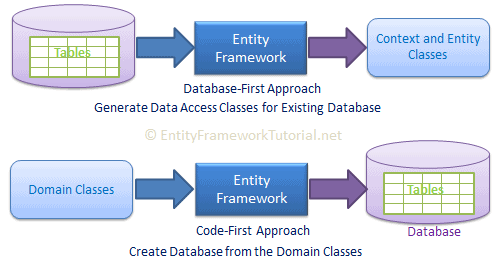
Code-First vs Database-First
There are two main ways to work with Entity Framework Core:
- Code-First: With the Code-First approach, you focus on coding your C# classes, and Entity Framework Core will create or update the database schema based on your models. This is suitable for new projects where the database doesn't exist yet, or when you want your C# classes to drive the database design.
- Database-First: With the Database-First approach, you start with an existing database, and Entity Framework Core will create the corresponding model classes based on the database schema. This is suitable for existing projects where the database design already exists and drives the C# classes creation.
CRUD Operations
Entity Framework Core makes it very straightforward to perform Create, Read, Update, and Delete (CRUD) operations against your database.
- Creating Records: You can create new records in the database by creating instances of your model classes and adding them to the DbSet, then calling
SaveChangeson your DbContext.
For example createEmployee endpoint from project last week:
- Reading Records: You can read records from the database using LINQ queries.
- Updating Records: You can update records in the database by fetching them into your application, modifying properties, and then calling
SaveChanges.
For example: updateEmployee endpoint
- Deleting Records: You can delete records by fetching them into your application, removing them from the DbSet, and then calling
SaveChanges.
For example deleteEmployee endpoint
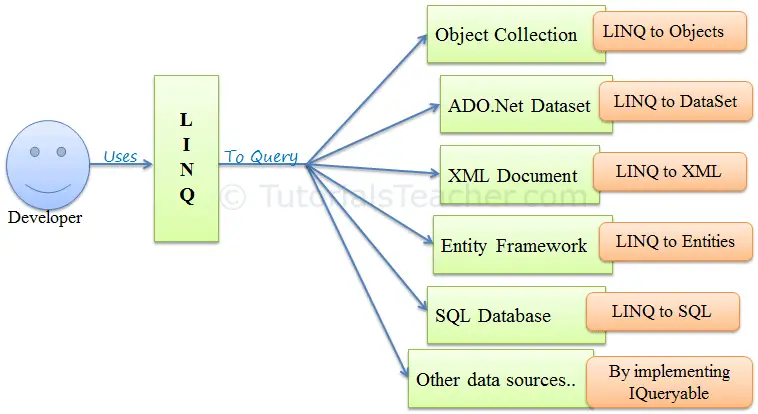
Using LINQ for Data Access
LINQ (Language Integrated Query) is a powerful querying language for .NET, and one of the main benefits of using EF Core is that it allows you to use LINQ to query your database. The LINQ queries you write are translated into SQL by EF Core and sent to the database.
For more detail:
- Diagrams showing how Entity Framework Core works: https://www.entityframeworktutorial.net/efcore/entity-framework-core.aspx