Understanding CLR, CTS, and CLS
Understanding CLR, CTS, and CLS
In .NET, the Common Language Runtime (CLR), the Common Type System (CTS), and the Common Language Specification (CLS) are important components that facilitate language interoperability, code execution, and type safety.
CLR (Common Language Runtime)
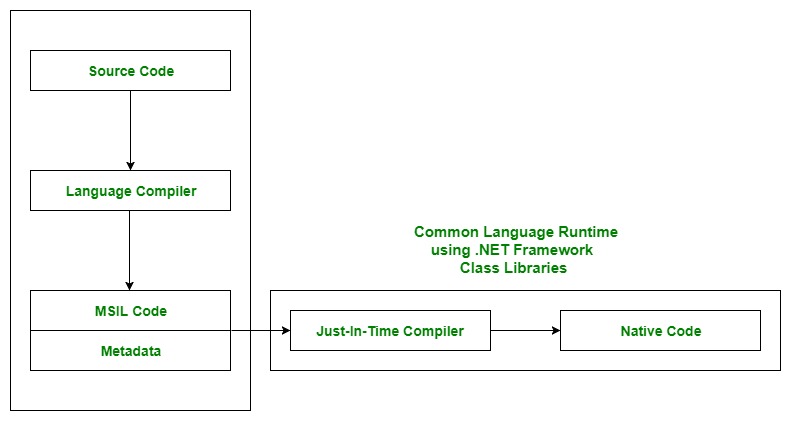
The CLR is the runtime environment provided by the .NET Framework, which executes the code written in any .NET programming language. The CLR provides various services like garbage collection, exception handling, and security. In essence, it's responsible for managing the execution of .NET programs regardless of which .NET programming language they were written in.
CTS (Common Type System)
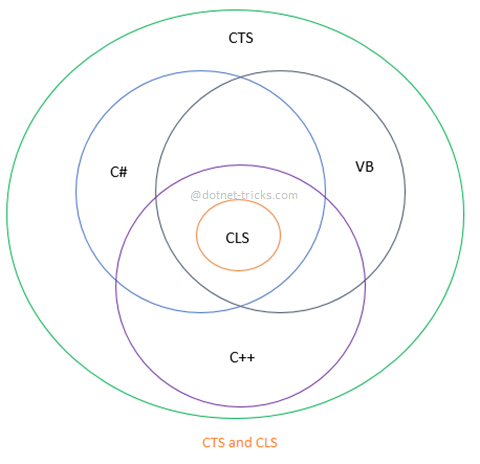
The CTS is a standard that specifies how types are declared, used, and managed in the runtime, and it's intended to ensure that types are portable across all .NET languages. For example, the int type in C# is equivalent to Integer in VB.NET, thanks to the CTS.
The CTS also ensures that objects written in different .NET languages can interact with each other. For instance, you can use a C# library in a VB.NET program.
CLS (Common Language Specification)
The CLS is a subset of the CTS and defines a set of rules that all .NET languages must follow. It's basically a set of specifications that allows different .NET languages to be interoperable and interact seamlessly with each other. This means that you can use one .NET language to build a part of your application and another .NET language to build another part, and the two parts will work together seamlessly.